Pima Indians Diabetes Database
Predicting the onset of diabetes based on diagnostic measures
Data: This dataset is originally from the National Institue of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. All patients (768) here are females at least 21 years old of Pima Indian Heritage. The dataset consist of several medical predictor variables and one target.
Independent variables
- Pregnacies (preg): Number of pregnancies the patients
- Body-Mass-Index (BMI) in kg/m^2
- Glucose level (glu): Plasma glucose concentraion a 2 hours in an orgal glucose tolerance test
- Blood Pressure (bp): Diastolic blood pressure in mmHg
- Skin Thickness (skin): Triceps skin fold thicknes in mm
- Insulin level (insulin): 2-hour serum insulin (micro-U/ml)
- Diabetes pedigree function (dpfunc)
- Age (age) in Years
Target Varibales
- Outcome (Y): Class varible (0 or 1)
Data source: https://www.kaggle.com/uciml/pima-indians-diabetes-database/home
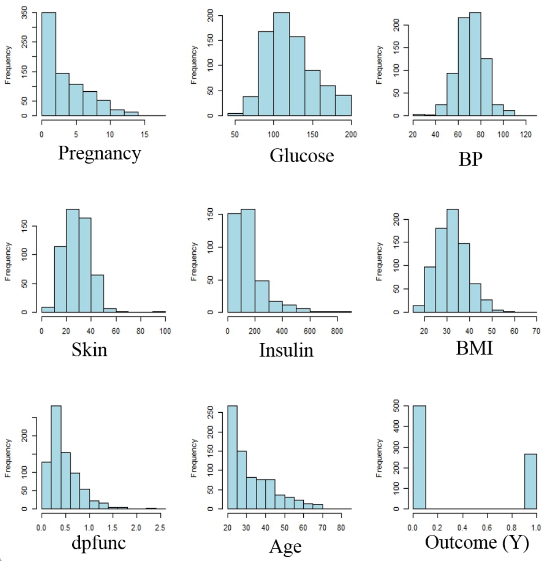
Histograms of predictors
Summary Statistics
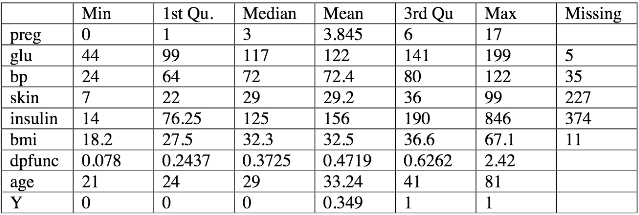
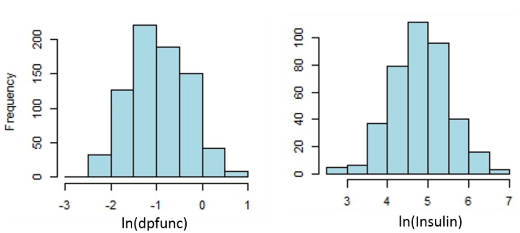
Missing values can be found in glu, bp, skin, insulin, and bmi, columns as “0”. Rows with these missing values were assigned NA. The distribution of predictors and their summary statistics are shown in figure-1 and table-1, respectively. Except BMI, BP, glucose, and skin, distributionns of all other predictors are strongly skewed. Mean and median values are found to be very close for bmi (32.3, 32.5), bp (72, 72.4) distributions (figure 1). The distribution of glu is slightly skewed. Log transformation of insulin and dbfunc predictors exhibit histrograms with normal distributions as shwon in figure 2. Skinwness of age variable can be cured taking the reciprocal of age.
Missing Data Imputation with WinBUGS
Data set was partitioned randomly considering 87% data in train set. Any missing row in test set was discared. Missing data in train set (glu, bp, skin, insulin, bmi variables) was considered for imputation with following the following model.
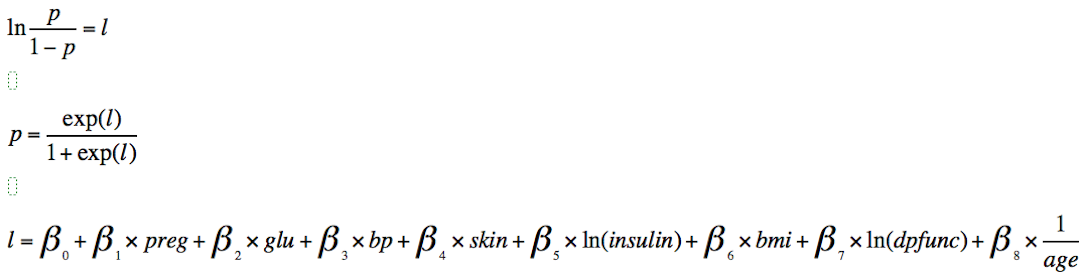
Classification model with WinBUGS
Bayesian Logistic Regression model was built to predict whether a patient is diabetic or not.
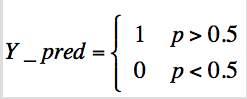
Model Evaluation
Confusion matrix is calculated from real outcome and predicted outcome. Accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and specificity were determined. The Bayesian logistic model can predict the outcome (Y) with 69% accuracy with 61% precision. The specificity of 82% suggests that the model is capable of predicting the patients that do not have diabetes than predicting patients with diabetics. Hence, model sensitivity needs to improved.

https://mwickram.github.io/pima-indian-diabetes/